Room temperature protocol. No ice bucket required.
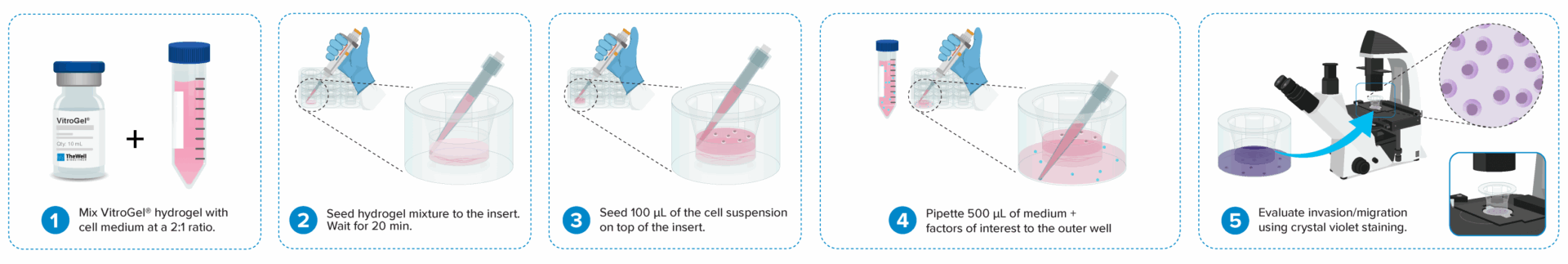
Can be done in 30-min. Room temperature stable protocol that can be adapted to laboratory automation.
VitroGel® Cell Invasion Assay Kit
A simple and easy replacement for animal-based ECM for consistent cell invasion studies.
This kit includes the VitroGel® Hydrogel Matrix with VitroPrime™ Cell Culture Inserts, 8 µm, PET
VitroGel® Cell Invasion Assay Kit (Ready-To-Use)
Your gateway for easy-to-use and consistent in-depth cell invasion studies.
Go beyond your traditional animal-based ECM for invasion studies with our xeno-free VitroGel® hydrogels and VitroPrime™ Cell Culture Inserts.

Adjust ECM composition
Manipulate the chemokines, cytokines, growth factors, etc., within the hydrogel matrix to understand their effects on cell mobility.

Consistent results
No batch-to-batch variability. A defined system without unknown protein composition to ensure robust results.

Support barrier models
The system can be used to create in vitro complex microenvironment models.

Excellent image quality
The membrane does not stain when performing common staining for imaging (i.e., crystal violet).
Accurate evaluation of studies
The kit includes our premium VitroPrime™ Cell Culture inserts with even pore sizes allowing more accurate and consistent invasion and migration studies.
Cell invasion, a vital process in various biological contexts, can be pivotal in embryonic development, immunosurveillance, and wound healing while also playing a concerning role in cancer metastasis. Traditional in vitro invasion assays have relied on animal-based extracellular matrices, which come with challenges like undefined components, batch-to-batch variability, and cumbersome temperature-sensitive protocols, thus leading to inconsistent and inaccurate studies.
The VitroGel® Cell Invasion Assay Kit is powered by VitroGel® hydrogel (versatile, xeno-free, bio-functional hydrogels that closely mimic the physiological extracellular matrix) and coupled with our premium quality VitroPrime™ Cell Culture Inserts, allowing more accurate and consistent invasion and migration studies than animal-based ECM.
The VitroGel® Cell Invasion Assay Kit (Ready-To-Use) in this page (includes our VitroGel® Hydrogel Matrix) is an optimal choice to simply replace the animal-based ECM for most traditional cell mobility studies. The nature of this synthetic system also allows researchers to precisely design the experiment by adjusting supplements and desired factors within the hydrogel matrix.
We also provide tunable VitroGel® High-Concentration Cell Invasion Assay Kit, which offers unmatched flexibility, allowing researchers to fully customize the hydrogel matrix—adjusting mechanical strength, binding ligands, and ECM components. No other product enables such a deep exploration of cell mobility and invasion studies, providing researchers with the precision and control needed to push the boundaries of their experiments like never before. Learn about our tunable VitroGel® High-Concentration Cell Invasion Assay Kits >
Specifications
| Use | Cell Invasion, cell migration, co-culture, barrier model |
| Inserts | VitroPrime™ Cell Culture Inserts 8 µm, PET, Transparent, Sterile |
| Kit Contents | VitroGel® Hydrogel Matrix + VitroPrime™ Cell Culture Inserts in a 24-well plate |
| Formulation | Xeno-free, functional hydrogel |
| pH | Neutral |
| Storage | Store hydrogel at 2-8°C. Ships at ambient temperature |
Cell invasion culture process in 30 minutes.
Work confidently at room temperature. No ice bucket required. VitroGel® Cell Invasion Assay Kit is ready-to-use. There is no cross-linking agent required.
Learn how gelation works.
Type of studies capable with VitroGel® Cell Invasion Assay Kit (Ready-To-Use)
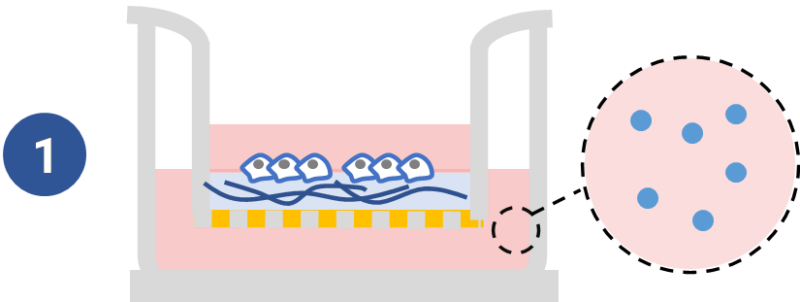
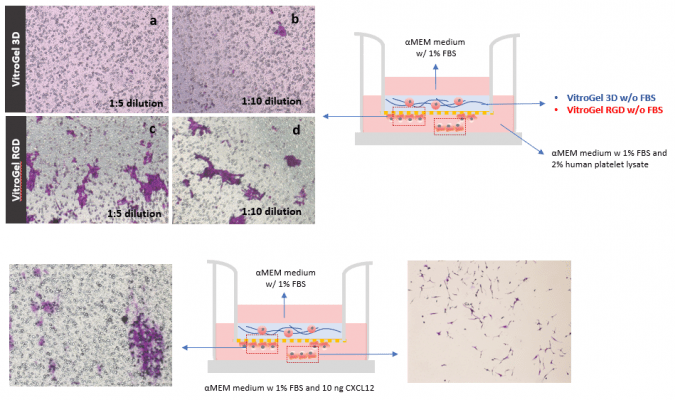
Study traditional invasion assay of chemoattraction from outer well.
Adding chemoattractants into the outer well to study cell mobility with ready-to-use VitroGel® Hydrogel Matrix system.
See example >
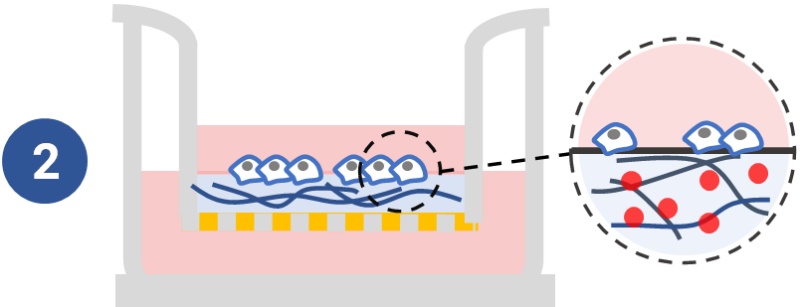
Study the effect of cytokine /supplement of hydrogel matrix on cell mobility.
Manipulate the chemokines, cytokines, growth factors, etc., within the hydrogel matrix to understand their effects on cell mobility. See example >


Unique Application to VitroGel® With VitroGel®-based Cell Invasion Assay Kits, not only you can perform traditional invasion/migration assays but go beyond to study more types of invasion/migration studies with the tunable kits. Learn about our tunable VitroGel® High Concentration Cell Invasion Assay Kits >
Comparison of VitroGel® versus traditional animal-based ECM for cell invasion studies
Ready-To-Use VitroGel®-Based Cell Invasion Assay | Traditional assay with animal-based ECM |
|
Operation temperature | Room temperature | 2-8 °C |
Set up time | 30 mins | 2 hours + |
Control compounds of outer well | ✔ | ✔ |
Consistent results | ✔ | ― |
Control key compounds in hydrogel | ✔ | ― |
Control mechanical strength of hydrogel | ― | ― |
Study functional ligands of hydrogel | ― | ― |
Control hydrogel degradation | ― | ― |
High-throughput / Lab automation | ✔ | ― |
Protocols and Resources
Videos & Webinars
Application Notes
Research Highlights
Data and References
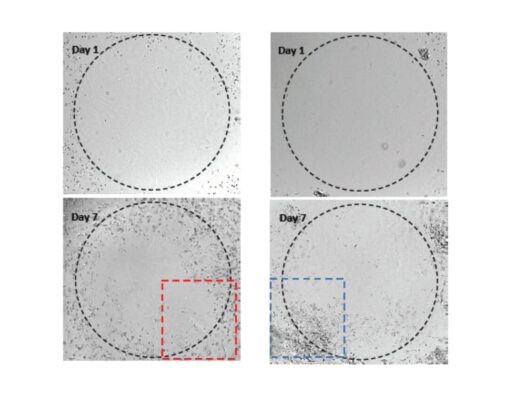
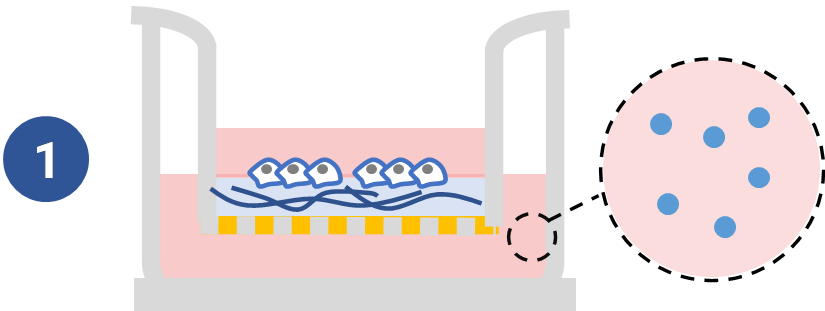
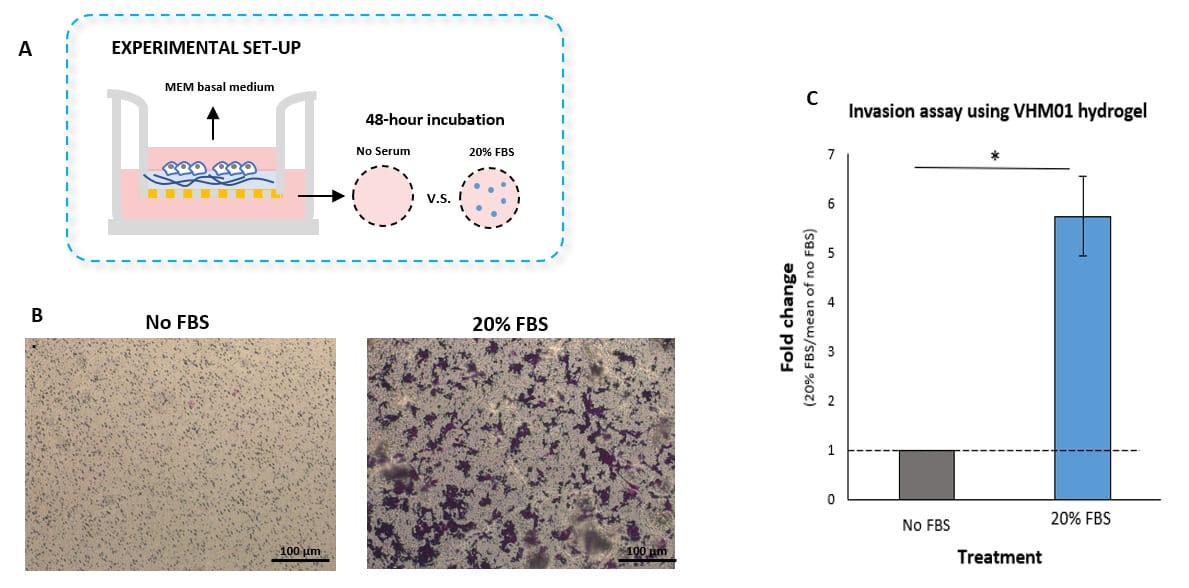
Invasion of U87-MG Glioblastoma cells towards an FBS gradient
- Cell Invasion Assay Kit: VitroGel® Cell Invasion Assay (Ready-to-use, Cat # IA-VHM01-4P)
- Insert: VitroGel® Hydrogel Matrix
- Outer well: No serum v.s. 20% FBS
- Cell incubation time: 48 hrs
Invasion of U87-MG glioblastoma cells through VitroGel® Hydrogel Matrix caused by a serum gradient.
A. Schematic representation demonstrating the invasion assay cell culture set-up. B. U-87 MG cell invasion was visualized by performing crystal violet staining followed by light microscopy. The images show the membrane inserts from control group (No FBS) and 20% FBS conditions. Images were obtained with a Zeiss microscope at a 10X magnification. C. Fold change of U87-MG cell invasion between control and 20% FBS groups. The control group was normalized to 1. The asterisk (*) stands for p<0.05.

Take Advantage of the Synthetic Nature and Well Characterized Composition of VitroGel® And Assay Growth Factor and Drugs within the Hydrogel
- Cell Invasion Assay Kit: VitroGel® Cell Invasion Assay (Ready-to-use, Cat # IA-VHM01-4P)
- Insert: VitroGel® Hydrogel Matrix with TGF-β1 v.s. without TGF-β1
- Outer well: No serum v.s. 20% FBS
- Cell Incubation time: 24 hrs
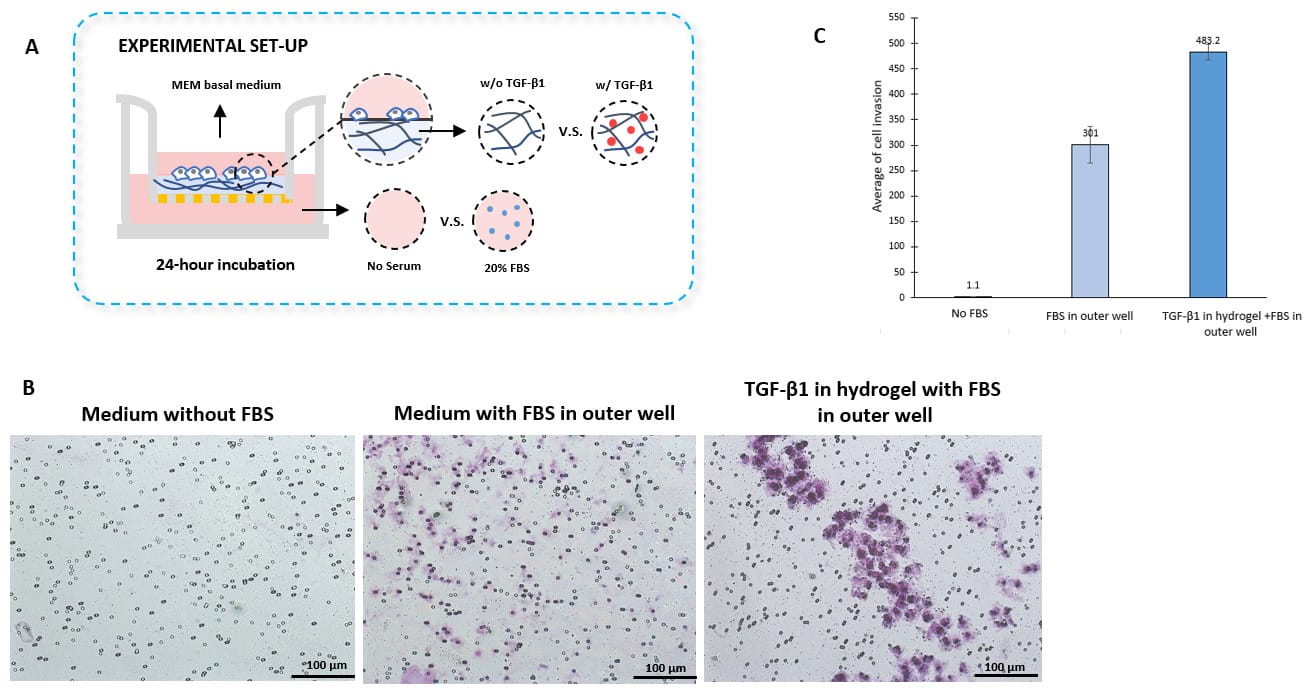
TGF-β1 inside of VitroGel® hydrogel matrix induces invasion of U87-MG glioblastoma cells.
A. Visual representation of invasion assay setup. B. Light microscopy images demonstrating cell invasion in the different groups after crystal violet staining. Images were obtained with a Zeiss microscope at a 10X magnification. C. Mean of U87-MG cell invasion for each of the experimental conditions.
References/Publications
- Chen, Y.-C., Takada, M., Aerica Nagornyuk, Yu, M., Yamada, H., Nagashima, T., Masayuki Ohtsuka, DeLuca, J. G., Markus, S. M., Motoki Takaku, & Suzuki, A. (2025). Inhibition of p38-MK2 pathway enhances the efficacy of microtubule inhibitors in breast cancer cells. ELife, 13. https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.104859.3
- Sung, Y.-N., Kim, M.-J., Jun, S.-Y., Kim, Y. W., Park, J., Jang, S.-W., Song, T. J., Song, K. B., & Hong, S.-M. (2025). Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 as a biomarker of venous invasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. American Journal of Cancer Research, 15(3), 1248–1263. https://doi.org/10.62347/ovuj4436
- Li, H., Hou, M., Zhang, P., Ren, L., Guo, Y., Zou, L., Cao, J., & Bai, Z. (2024). Wedelolactone suppresses breast cancer growth and metastasis via regulating TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpp/rgae065
- Baik, J., Lee, M., Jae Hong Yoo, Jo, A., & Han, K.-S. (2024). Induction of glioblastoma invasion triggered by system Xc−-mediated glutamate release. Molecular & Cellular Toxicology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-024-00433-x
- Shi, L., Yang, D., Dong, H., Zhang, X., & Yang, C. (2024). miR-34b-5p suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in endometrial cancer AN3CA cells by targeting ZEB1. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, 17(4), 137–150. https://doi.org/10.62347/JVBV7887
- Morelli, M., Lessi, F., Franceschi, S., Ferri, G., Giacomarra, M., Menicagli, M., Gambacciani, C., Pieri, F., Pasqualetti, F., Montemurro, N., Paolo Aretini, Orazio Santo Santonocito, Luisa, A., & Chiara Maria Mazzanti. (2024). Exploring Regorafenib Responsiveness and Uncovering Molecular Mechanisms in Recurrent Glioblastoma Tumors through Longitudinal In Vitro Sampling. Cells, 13(6), 487–487. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13060487
- Dong Hee Lee, Ahn, H., Hyun Sang Sim, Choi, E., Choi, S.-H., Jo, Y., Bong Sik Yun, Hyun Kyu Song, Soo Jin Oh, Kaori Denda-Nagai, Park, C.-S., Tatsuro Irimura, Park, Y., & Jin, H. (2023). A CRISPR activation screen identifies MUC-21 as critical for resistance to NK and T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 42(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-023-02840-9
- Venuta, A., Nasso, R., Gisonna, A., Iuliano, R., Montesarchio, S., Acampora, V., Sepe, L., Avagliano, A., Arcone, R., Arcucci, A., & Ruocco, M. R. (2023). Celecoxib, a Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug, Exerts a Toxic Effect on Human Melanoma Cells Grown as 2D and 3D Cell Cultures. Life, 13(4), 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13041067
- Manferdini, C., Trucco, D., Saleh, Y., Gabusi, E., Dolzani, P., Lenzi, E., Vannozzi, L., Ricotti, L., & Lisignoli, G. (2022). RGD-Functionalized Hydrogel Supports the Chondrogenic Commitment of Adipose Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Gels, 8(6), 382. https://www.mdpi.com/2310-2861/8/6/382/
| Assay Kit Configuration | 1 mL + (12) VitroPrime™ Cell Culture Inserts, 4 mL + (48) VitroPrime™ Cell Culture Inserts |
|---|