VitroGel® IKVAV High Concentration
Laminin-derived functional peptide (IKVAV) modified – tunable, xeno-free hydrogel, high concentration ( 3 mL kit)
VitroGel IKVAV High Concentration
VitroGel® IKVAV High Concentration is a tunable, xeno-free (animal origin-free) hydrogel system modified with laminin-derived functional peptide (IKVAV). IKVAV is the bioactive sequence located on the C-terminal end of the long arm of the α‐1 chain of laminin, which is actively involved in different biological activities such as neuronal progenitor cell differentiation, promoting cell adhesion, neurite outgrowth, angiogenesis, and tumor growth. VitroGel IKVAV High Concentration comes with VitroGel Dilution Solution to adjust the final hydrogel strength from 10 to 4000 Pa.
VitroGel High Concentration hydrogels are our xeno-free, tunable hydrogels for researchers wanting full control to manipulate the biophysical and biological properties of the cell culture environment. The tunability of the hydrogel gives the ability to create an optimized environment for cell growth. The hydrogel system has a neutral pH, transparent, permeable and compatible with different imaging systems. The solution transforms into a hydrogel matrix by simply mixing with the cell culture medium. No cross-linking agent is required. Cells cultured in this system can be easily harvested with our VitroGel® Cell Recovery Solution. The hydrogel can also be tuned to be injectable for in vivo studies.
From 3D cell culture, 2D cell coating to animal injection, VitroGel makes it possible to bridge the in vitro and in vivo studies with the same platform system.
Mix & Match – 3D Cell Culture Your WAY!
![]() Unique to VitroGel High Concentration hydrogels is the ability to tailor create a multi-functional hydrogel by blending different types of VitroGel. VitroGel® IKVAV can be “mix & matched” with other versions of VitroGel such as VitroGel® RGD, VitroGel® YIGSR, VitroGel® MMP and VitroGel® COL to create the customized multi-functional hydrogel. Using this flexible and powerful hydrogel system, scientists can customize their 3D culture micro-environment for different applications.
Unique to VitroGel High Concentration hydrogels is the ability to tailor create a multi-functional hydrogel by blending different types of VitroGel. VitroGel® IKVAV can be “mix & matched” with other versions of VitroGel such as VitroGel® RGD, VitroGel® YIGSR, VitroGel® MMP and VitroGel® COL to create the customized multi-functional hydrogel. Using this flexible and powerful hydrogel system, scientists can customize their 3D culture micro-environment for different applications.
Specifications
| Contents | VitroGel® IKVAV High Concentration, 3 mL VitroGel® Dilution Solution, 50 mL |
| Hydrogel Formulation | Xeno-free tunable hydrogel modified with IKVAV peptide. |
| Use | Support neuronal progenitor cells differentiation, promoting cell adhesion, neurite outgrowth, angiogenesis, and tumor growth |
| Mix & Match | Can be blended with other versions of VitroGel concentrated hydrogels to create a custom multi-functional matrix. |
| Operation | Room temperature |
| Hydrogel Strength | 10 to 4,000 Pa of G’ depending on dilution ratio. Dilute with VitroGel Dilution Solution (TYPE 1 or TYPE 2) for different concentrations. |
| pH | Neutral |
| Color | Transparent |
| Cell Harvesting | VitroGel Organoid Recovery Solution 5-15 min cell recovery |
| Injectable | Injectable hydrogel |
| Storage | Store at 2-8°C. Ships at ambient temperature |
| Number of Uses | Dilution ratio: 1:2 = 225 uses at 50 µL per well 1:3 = 300 uses at 50 µL per well 1:5 = 450 uses at 50 µL per well |
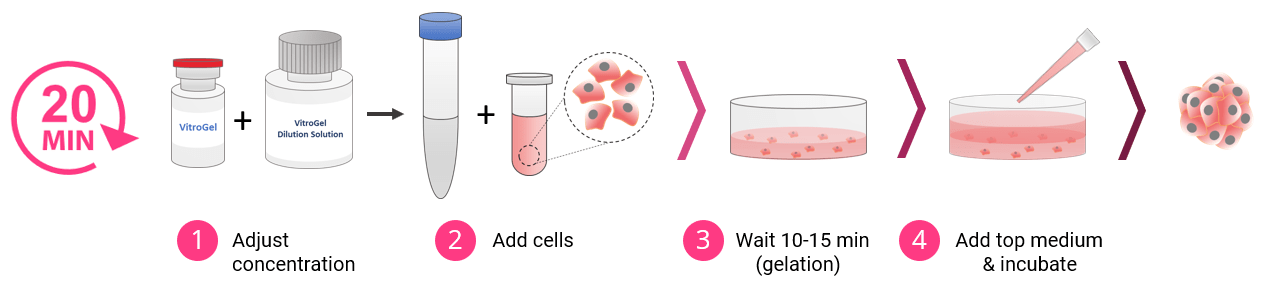
3D Cell Culture Process in 20 Minutes
VitroGel High Concentration hydrogels are easy-to-use. There is no cross-linking agent required. Work confidently at room temperature.
Tunable Hydrogel Strength
Simply diluting the hydrogel controls the gel strength.
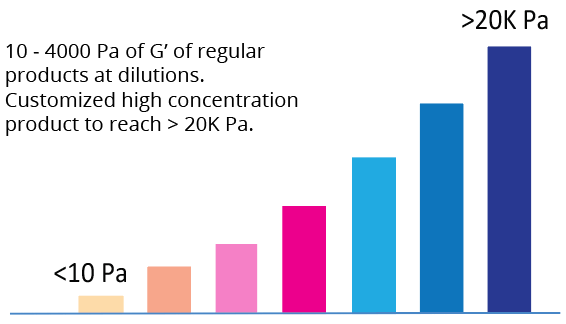
Protocols / Handbooks / Resources
Video Protocols & Demonstrations
Data and References
Cell Type Behavior Reference Table – VitroGel IKVAV
Multiple uses of immobilized, conjugated IKVAV in different tissue and cell type. IKVAV has been used as an immobilized, adhesive substrata for multiple cell types to study many different cellular processes and behaviors in normal physiological and pathological contexts.
| Cell Type | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Glioma LRM55 | Promoted cell attachment |
| Melanoma A2058 | Increased type IV collagenolytic activity |
| Melanoma K-1735 | Increased cell invasion |
| Melanoma SK-MEL-28 | Increased cell adhesion and proliferation |
| Prostate PC3 | Increased cell growth and invasion |
| Cell Type | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Rat skin fibroblasts | Increased cell adhesion |
| Cell Type | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Pulmonary fibroblasts LL29 | Increased cell adhesion |
| Cell Type | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Human neural stem cells | Promoted cell viability and differentiation |
| Mouse neural progenitor cel | Promoted cell adhesion and differentiation |
| Mouse spiral ganglion neurons | Promoted neurite outgrowth |
| Neural PC12 | Promoted neurite outgrowth |
| Rat cortical astrocytes | Increased cell adhesion |
| Rat neural stem cells | Promote cell attachment and differentiation |
| Cell Type | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Β-cells MIN6 | Increased insulin release and reduced apoptosis |
| Cell Type | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Human adipose derived stem cells | Increased cell attachment |
| Human mesenchymal stem cells | Increased cell viability |
| Human mesenchymal stem cells | Promoted neuronal differentiation |
| Cell Type | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Human umbilical vein endothelial cells | Increased cell infiltration |
| Human outgrowth endothelial cells and bone | Promoted angiogenesis |
| marrow mesenchymal stem cells |
| TISSUE/ORGAN TYPE | CELL TYPE | READY TO USE | HIGH CONCENTRATION | BEHAVIOR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta Cell | BL5 human beta cells | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel 3D, VitroGel MMP | Enhance spheroids formation |
| Beta TC3 cells | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation and cellular interactions | |
| Bone | Bone marrow stromal cells (rat) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel MMP | Osteogensic differentiation , Cell attachment and osteoblast differentiation,Cell proliferation, cell viability, and cellular networking. |
| Osteoblasts (rat) | VitroGel MSC, VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Cell attachment and spreading | |
| Bone marrow stromal cells (bovine) | VitroGel MSC, VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Cell spreading and osteocalcin expression | |
| Breast | Mammary gland MCF10A | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitrolGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel MMP | Spheroid formation, MMP activity in response to TGF-B1 |
| Mammary epithelium (mouse) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Cell invasion and dissemination | |
| Cancer/Tumor | Human colorectal carcinoma HCT 116 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation, cell survival, and intercellular networking |
| Huaman colon carcinoma HCT-8 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation and cell matrix interaction | |
| Glioma U87-MG | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel MMP, VitroGel COL | Cell spreading and acting stress fiber assembly, cell proliferation, spreading, and migration, Cell migration dependent on mechancial force, Cell proliferation and cell matrix interaction | |
| Gliobastoma SF 268 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitrolGel RGD | Cell proliferation and cell matrix interaction | |
| Gliobastoma SF 295 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation and cell matrix interaction | |
| Glioblastoma SNB75 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation and cell matrix interaction | |
| Glioblastoma U-251 MG | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation and cell matrix interaction | |
| Prostate PC3 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel COL, VitroGel IKVAV, VitroGel RGD, VitroGel MMP | Cell proliferation, reduced MMP release, invasion, migration, and spheroid metabolic activity. | |
| Prostate LNCaP | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Cell attachment, proliferation, and prostate specific antigen release | |
| Prostate CRPC | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation and invasion | |
| Prostate DU145 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation and invasion | |
| Melanoma B16F10 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel COL, VitroGel YIGSR | Cell migration, invasion, MMP release, cell attachment and spreading | |
| Breast MDA-MB-231 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel MMP, VitroGel 3D | Cell invasion, spreading, proliferation, division, migration, and cluster growth | |
| Fibrosarcoma HT1080 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Cell infiltration, attachment | |
| Breast T47D | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel COL, VitroGel 3D, VitroGel RGD, VitroGel MMP | Force dependent tubule formation, cell cluster growth, spheroid formation and proliferation | |
| Breast 4T1 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation | |
| Breast CTC | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel 3D, VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation | |
| Breast E0771 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation spheroid formation | |
| Brest AU-565 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation cell matrix interactions | |
| Epithelial ovarian OV-MZ-6 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Spheroid formation and proliferation | |
| Epithelial ovarian SKOV-3 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Spheroid formation and proliferation | |
| Glioma U373-MG | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel MMP | Cell adhesion, invasion and migration | |
| Rhabdomyosarcoma (human) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel YIGSR | Cell attachment and spreading | |
| Melanoma SK-MEL-28 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel IKVAV | Cell adhesion and proliferation | |
| Melanoma K-1735 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel IKVAV | Cell invasion | |
| Melanoma A2058 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel IKVAV | Collagenolytic activity | |
| Brainstem glioma DIPG | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel MMP | Cell proliferation and survival | |
| Hela Cells | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel 3D, VitroGel RGD, VitroGel MMP | Cell proliferation | |
| Colorectal adenocarcinoma DLD-1 cells | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation and cell matrix interaction | |
| Giloma LRM55 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel IKVAV, VitroGel MMP | Cell attachment | |
| Melanoma WM 239A | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel MMP | Cell invasion | |
| Melanoma Cells | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation and cell matrix interaction | |
| Insulinoma ins-1 (Rat) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation and cell matrix interaction | |
| Biphasic synovial sarcoma SYO-1 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation, cell matrix interation, and cell survival | |
| Fuji Cells | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation and cell matrix interaction | |
| Chordoma Cells | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel 3D | Cell proliferation | |
| Bone OSA 1777 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Spheroid and cluster formation | |
| Glioma RuGli | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel COL | Integrin dependent cell adhesion | |
| Breast Cancer MCF-7 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel MMP, VitroGel 3D | Cell proliferation, intercellular connections, morphological changes, MMP expression, and angiogenesis | |
| Liver carcinoma HepG2 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Cell viability, growth, drug resistance, proliferation, and cellular matrix interaction | |
| Human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel MMP | Cell proliferation and cellular interactions | |
| Primary breast (human) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel MMP | Cell invasion, migration, and dissemination | |
| Ovarian carcinoma OVCAR-3 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel MMP | Cell proliferation, cell matrix interactions | |
| Ovarian OVCA429 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel MMP, VitroGel COL | MMP dependent cell invasion | |
| Human Osteosarcoma KHOS | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel 3D | Cell proliferation and spheroids formation | |
| Human Osteosarcoma U2OS | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel 3D | Cell proliferation and spheroids formation | |
| Human fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel 3D | Cell proliferation and inflammatory responses | |
| Human Liposarcoma 94T778 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel 3D | Cell proliferation and spheroids formation | |
| Human diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBLC) SUDHL-10 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix | Cell viability, growth, drug resistance, proliferation, and cellular matrix interaction | ||
| Priess human lymphoblastoid cells | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel 3D | Enhance spheroids and cluster formation and promote cell viability. | |
| Cartilage | Chondrocytes (bovine) | VitroGel MSC, VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Cell viability and proliferation |
| Chondrocytes (human) | VitroGel MSC, VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Cell viability and proliferation | |
| Connective Tissue | Dermal Fibroblasts (human) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell viability and spreading |
| Fibroblasts NIH3T3 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Directional cell migration toward gradient and cell spreading dependent on substrata rigidity | |
| Foreskin fibroblasts (human) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel YIGSR, VitroGel MMP | Cell spreading, substrata degradation, and cell invasion | |
| Skin fibroblasts (skin) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel IKVAV | Cell adhesion | |
| Epidermal keratinocytes | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Cell viability | |
| Epithelial Cells | Mouse ovarian follicle cells | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | 3D cell culture using ES-hydrogel can enhance vitro follicle culture by considering the permeability and stiffness of the gel. |
| Human Nthy-ori 3-1 cells | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel 3D | Enhance spheroids and cluster formation and promote cell viability. | |
| A549 cells | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Enhance cell proliferation and cell matrix interactions. | |
| MCF-12A | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Enhance cell proliferation and cell matrix interactions. | |
| Immortalized bronchial epithelial cells HBEC-KRAS | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel 3D | Cell proliferation | |
| Eye | Corneal endothelial B4G12 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit, VitroGel Angiogenesis Assay | VitroGel RGD, Vitrogel Angiogenesis Assay HC kit | Cell attachment and spreading |
| Retinal ganglion cells (xenopus) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Neurite outgrowth | |
| Immune Cells | CD8 + T cells | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel 3D | Enhance spheroids and cluster formation and promote cell viability. |
| Kidney | Human embryonic kidney HEK293 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel HEK293, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | 3D spheroids formation |
| Madin-Darby Canine Kidney | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel HEK293, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel MMP | Epithelial cysts formation | |
| Podocytes (human) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel HEK293, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Glomerular capillary formation |
|
| glomerular endothelial cells (human) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel HEK293, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit, VitroGel Angiogenesis Assay | VitroGel RGD, Vitrogel Angiogenesis Assay HC kit | Glomerular capillary formation |
|
| Liver | Hepatocytes (human) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Filopodia formation and synthesis of albumin and cell attachment |
| Hepatocytes (mouse, rat, swine) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel MMP | Cell viability, spearding, Albumin secretion | |
| Lung | Alveolar basal epithelial A549 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell attachment |
| Alveolar epithelial RLE-6TN | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell attachment and mesenchymal differentiation | |
| Pulmonary fibroblasts LL2 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel IKVAV | Cell adhesion | |
| HFL1 lung fibroblasts CCL153 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell proliferation and spindle morphology | |
| Lung cancer associated fibroblasts (human) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Substrata contractility | |
| Lung fibroblasts MCR-5 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | NGF-mediated substrata contraction | |
| Muscle | Myoblasts C2C12 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Cell proliferation, differentiation, attachment, myofibril formation, myotube formation, and integrin dependent cell adhesion |
| Skeletal myoblasts (mouse) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD | Cell attachment, proliferation, and myofibril formation | |
| Myoblasts (human) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Cell adhesion, alignment along fiber, and myotube formation | |
| Myoblasts C25Cl48 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Cell proliferation, differentiation and myotube formation | |
| Neural | Dorsal root ganglion (chick) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL | Neurite formation and force dependent neurite outgrowth |
| Neural PC12 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel IKVAV | Neurite outgrowth | |
| Neural stem cell/ progenitor cell (rat) | VitroGel STEM, VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel IKVAV | Cell viability, attachment, and differentiation | |
| Neural stem cell/ progenitor cell (human) | VitroGel STEM, VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel IKVAV, VitroGel COL | Cell viability, attachment, and differentiation | |
| Schwann cells (rat) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix | VitroGel RGD | Cell attachment and migration | |
| Neural stem cell/ progenitor cell (mouse) | VitroGel STEM | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel IKVAV | Cell adhesion and differentiation | |
| Cortical astrocytes (rat) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel IKVAV | Cell adhesion | |
| Spiral ganglion neurons (mouse) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel IKVAV | Neurite outgrowth | |
| Motor neurons (human) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel IKVAV | Force dependent neurite outgrowth | |
| Forebrain neurons (human) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel IKVAV | Force dependent neurite outgrowth | |
| Cortical neurons (rat) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel IKVAV | Neuronal viability and neurite outgrowth | |
| Dorsal root ganglion (rat) | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel IKVAV | Neurite outgrowth | |
| Red Blood Cells | Red Blood Cells | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel 3D | Enhance Spheroids and cluster formation and promote cell viability |
| Pancreas | B-cells MIN6 | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel IKVAV | Reduced apoptosis and increased insulin release |
| Stem Cells | Mesenchymal stem cells (human) | VitroGel MSC | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel IKVAV, VitroGel MMP | Cell viability, proliferation, differentiation, neuronal differntiation, neurite outgrowth, attachment, spreading, viability, and osteoblast differentiation |
| Mesenchymal stem cells (mouse) | VitroGel MSC | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel MMP | Cell spreading and migration | |
| Mesenchymal stem cells (rat) | VitroGel MSC | VitroGel RGD | Cell adhesion and spreading | |
| Embryonic stem cells (mouse) | VitroGel STEM, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel COL, VitroGel YIGSR | Endothelial cell differentiation, neuronal differentiation, and neurite outgrowth | |
| Induced pluripotent stem cells (human) | VitroGel STEM, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel YIGSR, VitroGel IKVAV | Cell viability | |
| Human stem cells from apical papilla SCAP | VitroGel STEM | VitroGel RGD | Cell viability | |
| Hematopoietic Stem Cells | VitroGel STEM | Cell viability | ||
| Adipose derived stem cells (human) | VitroGel MSC | VitroGel RGD, VitroGel 3D, VitroGel IKVAV | Cell viability, cell attachment | |
| Vascular/cardiac | Umbilical vein endothelial cells | Vitrogel Angiogenesis Assay , VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | Vitrogel Angiogenesis Assay HC kit | Cell attachment, proliferation, migration, angiogenesis, gene expression changes, migratory cell infiltration, cell survival, and VEGF dependent migration |
| Neonatal cardiac (rat) | Vitrogel Angiogenesis Assay, VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix, VitroGel ORGANOID Kit | Vitrogel Angiogenesis Assay HC kit | Cell attachment, tissue regeneration, and attachment similar to laminin | |
| Aortic smooth muscle cells | VitroGel Hydrogel Matrix | Vitrogel Angiogenesis Assay HC kit | Cell attachment | |
| Endothelial (human) | VitroGel Angiogenesis Assay | Vitrogel Angiogenesis Assay HC kit | Cell differentiation | |
| Endotheliocytes | VitroGel Angiogenesis Assay | Vitrogel Angiogenesis Assay HC kit | Cell migration | |
| Microvascular endothelial cells (human) | VitroGel Angiogenesis Assay | Vitrogel Angiogenesis Assay HC kit | Cell mobility | |
| Aortic endothelial cells (bovine) | VitroGel Angiogenesis Assay | Vitrogel Angiogenesis Assay HC kit | Force dependent cell spreading | |
| Capillary endothelial cells (bovine) | VitroGel Angiogenesis Assay | Vitrogel Angiogenesis Assay HC kit | Capillary like network formation |
Data
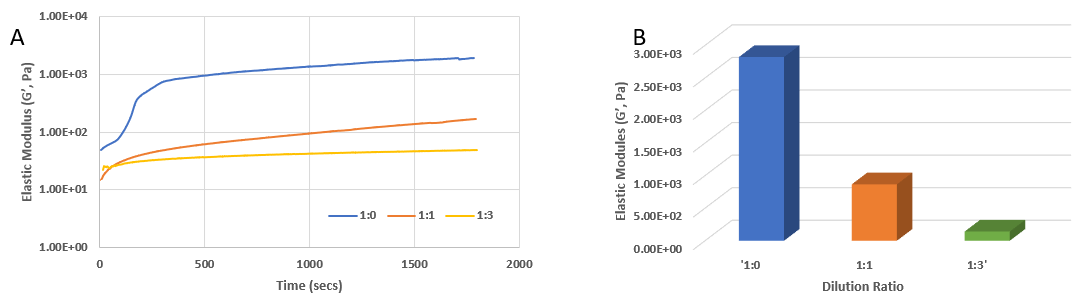
Figure 1. Rheological properties of VitroGel IKVAV with DMEM medium.
A) The gel formation curve after mixing with DMEM medium. VitroGel IKVAV was diluted at 1:0,1:1 and 1:3 (v/v) with VitroGel Dilution Solution (Type 1) and then mix with DMEM at 4:1 (v/v) ratio; B) The gel strength after 24 hrs incubation. The hydrogel was prepared as method A and incubated at 37°C CO2 incubator for 24 hrs before the rheological test. (10 ~ 4000 Pa of G’ of regular products at dilutions. Customized high concentration product to reach over 20K Pa)
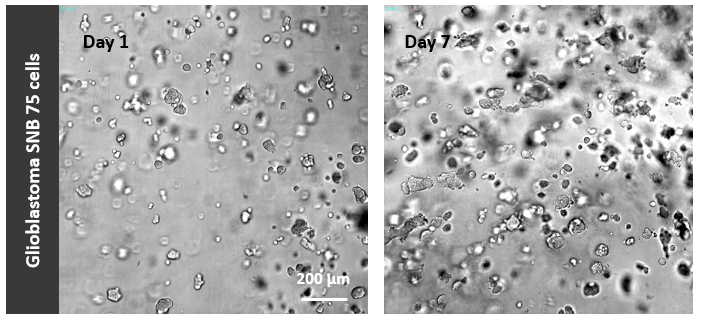
Figure 2. 3D culture of glioblastoma cells (SNB 75) in VitroGel IKVAV.
Cells were cultured with 1:3 diluted VitroGel IKVAV according to the user handbook (50% FBS was used to prepare cell suspension to achieve hydrogel with a final 10% FBS concentration).
Mix & Match Hydrogel System – 3D Cell Culture Your Way
Mix VitroGel IKVAV with VitroGel MMP at different ratios
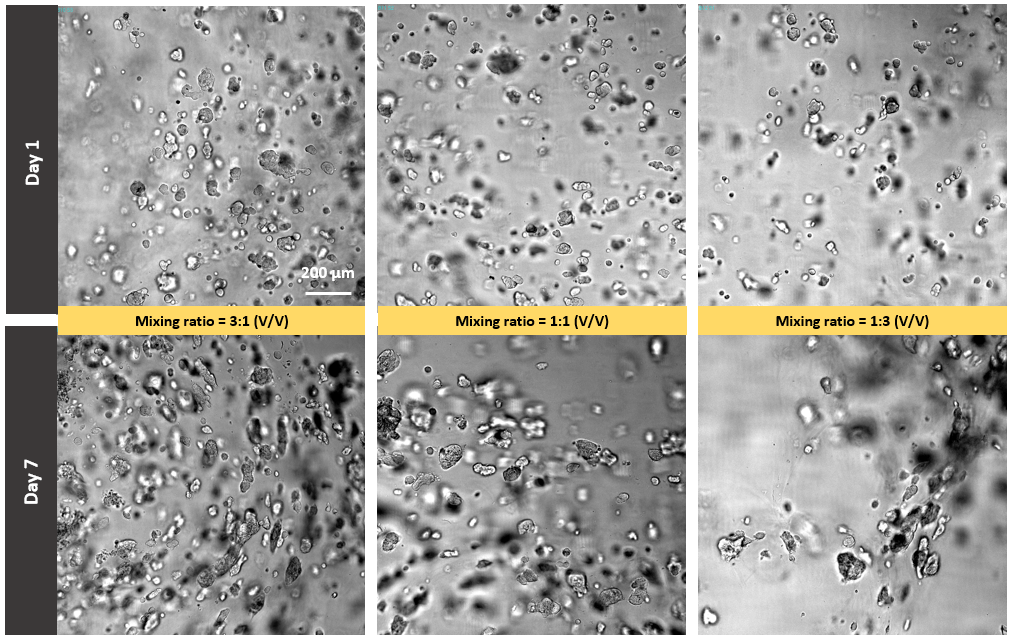
Figure 3. 3D culture of glioblastoma cells (SNB 75) in the mixture of VitroGel IKVAV and VitroGel MMP.
The mixing ratios of VitroGel IKVAV and VitroGel MMP are 3:1, 1:1 and 3:1 (V/V). Cells were cultured with a 1:3 diluted VitroGel mixture following the user handbook (50% FBS was used to prepare cell suspension to achieve hydrogel with a final 10% FBS concentration).
References/Publications
- DePalma, T., Rodriguez, M., Kollin, L., Hughes, K., Jones, K., Stagner, E., Venere, M., & Skardal, A. (2025). A Microfluidic Blood Brain Barrier Model to Study the Influence of Glioblastoma Tumor Cells on BBB Function. Small. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202411361
- Powell K. Adding depth to cell culture. Science, 356(6333), 96–98. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.356.6333.96
| High Concentration Kit Type | VitroGel IKVAV + Dilution Solution TYPE 1, VitroGel IKVAV + Dilution Solution TYPE 2 |
|---|